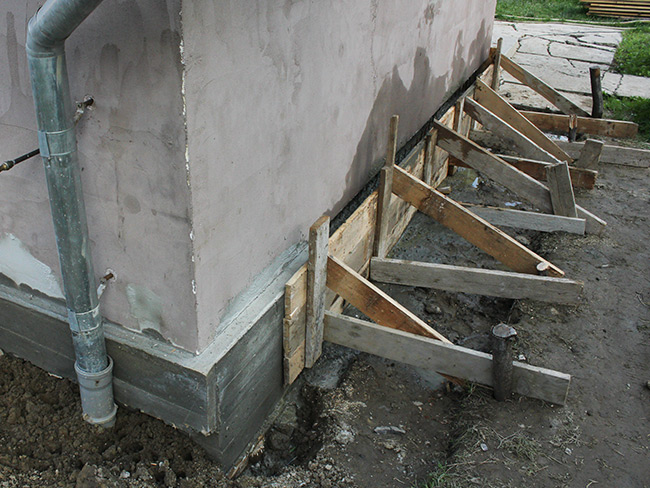
Underpinning is the practice of strengthening and stabilizing an existing foundation so it rests more securely on more supportive soil layers. Underpinning may become necessary if its purpose has shifted or additional loads have been added; underpinning should always be performed prior to any change being made or additional loads being introduced into an existing structure.
Underpinning Melbourne typically involves expanding a foundation’s depth or width so it rests on a wider area of supporting soil, providing support in both depth and breadth. There can be various reasons for doing this including:
Pin Method
Concrete underpinning involves installing new bored pier footings alongside the house at 2-to-3m centers around both its exterior and interior (known as concrete underpinning) for support of an existing house by strengthening, stiffening and lessening movement in future years. They do not address movement caused by changes in soil moisture content as this issue can be reversed later.
Soil is excavated in stages known as ‘pins’ until strata capable of supporting the load of the building is reached, after which concrete mixture is poured to form underpinning. Once underpinned, pins are connected to existing foundations using dry sand cement packing mortar which transfers load safely – this method provides low costs and no need for tenants to vacate the premises; additionally it’s perfect where access or pollution concerns exist.
Needle Method
This underpinning technique is similar to the pit method, but uses needle beams instead of piles for greater efficiency and economy. It is particularly useful if you require reinforcement but can only excavate part of a building’s foundation at once, and also save money on disposal fees for excavated soil.
Underpinnings designed to transfer load from an existing building onto a mass concrete foundation without disrupting existing foundation soil structures are key in avoiding structural damage or collapse of an existing building.
Needle underpinning can help resolve problems associated with soil settlement or the construction of new buildings near existing foundations. Furthermore, needle underpinning can improve bearing capacity in clayey or waterlogged soil that does not respond well to traditional or Jack pile underpinning methods.
Pile Method
Underpinning with piles is used to transfer loads from shallow foundations into deeper soil strata with greater bearing capacity, as well as to protect existing structures against excessive or differential settlement.
Piled underpinning is ideal in situations with environmental concerns or restricted access. Pile are driven into the ground at depths up to 15m either side of an existing wall and connected using needles (also called pile caps) that support it, thus relieving its load.
Pile methods may utilize either steel hammered piles or concrete poured into drilled holes as solutions for subsidence issues on your property. Both approaches have their own set of benefits for certain situations; which one best fits you will depend on the ground conditions at your location and its history of subsidence – this can be easily assessed using our free Home Checkup!
Mass Concrete Method
Mass concrete is a type of concrete used in large construction projects like dams. This form requires larger aggregates than ordinary concrete to reach strength. Furthermore, more cement must be added than usual in order to achieve strength – however this higher cost comes with many benefits like being able to resist extreme loads better.
One of the major considerations when working with mass concrete is heat produced from cement hydration. This heat can raise temperatures rapidly, creating temperature gradients within its structure that could eventually lead to cracking. Therefore, it is vital that temperature monitoring be kept up during curing process of mass concrete structures.
Intelligent sensors to record and read the temperature of mass concrete can help avoid damage, minimize delays, meet project specifications and ensure durability of this durable substance. In addition, such sensors provide valuable insight into its state as well as any future issues which might arise with it.